Understanding the Basics of Laser Welding Machine
What is a Laser Welding Machine?
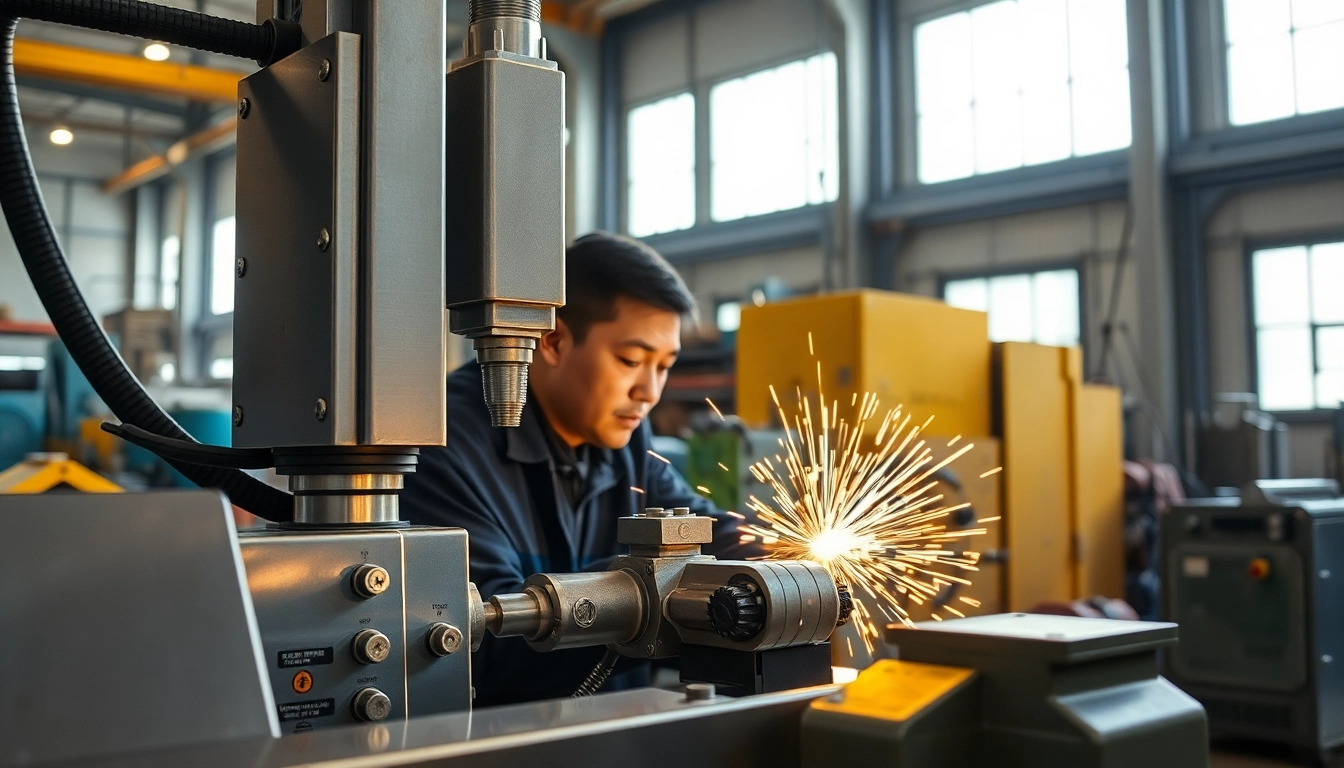
A Laser welding machine is an advanced tool that utilizes focused laser beams to join materials through a process called laser welding. Unlike traditional welding methods, which often involve heat from combustion or electric arcs, laser welding uses concentrated light energy to generate high temperatures precisely at the weld joint. This technology is rapidly gaining ground in various industries due to its precision, speed, and versatility.
The basic principle behind laser welding is the conversion of laser energy into heat, which melts the materials to be joined. The result is a high-quality weld with minimal distortion. Since it can be controlled with great accuracy, it is ideal for tasks requiring intricate work and thin materials.
Key Components of a Laser Welding Machine
Understanding the components of a laser welding machine is essential for both operation and maintenance. The main components include:
- Laser Source: This is the heart of the machine, responsible for generating the laser beam. Common types of laser sources used in welding include fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and solid-state lasers.
- Beam Delivery System: This component directs the laser beam from the source to the workpiece. It often includes lenses and mirrors that help focus the laser.
- Control System: Modern laser welding machines are equipped with sophisticated control systems that regulate various parameters such as power, speed, and focus. This technology allows for automation and integration with other systems.
- Cooling System: Given the high temperatures involved in laser welding, an efficient cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal operating conditions and prolonging machine life.
- Workholding Fixtures: These ensure that the workpieces are positioned accurately during the welding process, which contributes to the quality and repeatability of the weld.
Advantages of Using a Laser Welding Machine
Laser welding machines offer numerous advantages over traditional welding techniques:
- Precision: The focused laser beam allows for accurate and clean welding, making it ideal for intricate designs and thin materials.
- Speed: Laser welding is typically faster than conventional welding methods, which boosts productivity in manufacturing environments.
- Reduced Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): The concentrated energy of the laser significantly reduces the heat affected zone, minimizing distortion and altering material properties.
- Versatility: Laser welding can be used for a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics.
- Automation Potential: Laser welding machines can be easily integrated with robotic systems and automated manufacturing processes.
Applications of Laser Welding Machine in Industries
Aerospace and Automotive Applications
In both the aerospace and automotive industries, laser welding machines have revolutionized the manufacturing process. The ability to create strong, lightweight welds with minimal distortion is particularly advantageous where structural integrity is critical. Components such as airframe structures, engine parts, and control surfaces benefit from laser welding due to the high standards of safety and performance required.
Moreover, the efficiency of laser welding allows for reduced production times and the potential for lower labor costs. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting laser welding machines to meet stringent regulatory standards and improve overall accuracy in vehicle production.
Medical Device Manufacturing with Laser Welding Machine
The medical device industry demands precision and reliability, and laser welding machines deliver on both fronts. They are particularly beneficial in producing complex implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic devices. Laser welding offers the advantage of a low heat input, ensuring that the delicate properties of medical materials are preserved. This is crucial, especially in applications involving biocompatible materials.
Additionally, the versatility of laser welding allows manufacturers to create intricate shapes and structures that would be difficult to achieve with traditional welding methods, thereby expanding design possibilities in medical technology.
Consumer Electronics: The Role of Laser Welding Machine
In the consumer electronics sector, laser welding machines play a pivotal role in assembling devices such as smartphones, laptops, and smaller electronic components. High precision and the ability to work with micro-components make laser welding essential for creating reliable and durable products.
Furthermore, as consumer demands evolve, manufacturers leverage laser welding for rapid prototyping and innovative designs. The quick turnaround times associated with these machines facilitate agile manufacturing processes, allowing for faster entry of new products into the market.
Technical Considerations for Laser Welding Machine
Choosing the Right Laser Type for Your Needs
When selecting a laser welding machine, it’s essential to consider the type of laser it employs. The most common types include:
- Fiber Lasers: Known for their high efficiency and excellent beam quality, fiber lasers are versatile and suitable for various materials, particularly metals.
- CO2 Lasers: These lasers are ideal for welding non-metal materials like plastics and are generally less expensive to operate than fiber lasers.
- Solid-State Lasers: Although less common, solid-state lasers are beneficial for specific industrial applications, especially where high power output is necessary.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each laser type will ensure you select an appropriate system tailored to your operational requirements.
Power Settings and Their Importance
The power settings of a laser welding machine significantly influence the welding process and the quality of the final product. High power settings facilitate deeper penetration, enabling the welding of thicker materials. Conversely, lower power settings are suitable for thin materials to avoid excessive melting or burn-through.
Balancing power settings with welding speed and focus is crucial in achieving optimal results. An incorrect power setting may lead to insufficient weld strength or excessive heat-affected zones, necessitating a deep understanding of the materials involved and their welding characteristics.
Focus and Spot Size in Laser Welding Machine
Focus and spot size are critical parameters that directly impact the quality and efficiency of the welding process. A smaller spot size increases energy density, leading to higher temperatures and better penetrating power. However, this also requires more precision in the alignment of the components being welded.
Conversely, a larger spot size offers more flexibility but may not achieve the same depth of weld as a concentrated beam. Adjusting the focal length allows for greater control over the spot size and the overall heat distribution across the weld, contributing to the quality and integrity of the join.
Maintaining Performance of Your Laser Welding Machine
Regular Maintenance Practices
Like all precision machinery, laser welding machines require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Key maintenance practices include:
- Cleaning Optical Components: Regular cleaning of lenses and mirrors is crucial as contaminants can impair laser performance and lead to poor weld quality.
- Checking Alignment: Misalignment can result in ineffective welds; routine checks and adjustments are necessary to maintain precision.
- Monitoring Cooling Systems: Ensuring that cooling systems are functioning correctly prevents overheating and prolongs the machine’s lifespan.
- Software Updates: Many modern machines feature software controls that may require updates to enhance functionality and efficiency.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Even with proper maintenance, users may encounter issues with laser welding machines. Some common problems include:
- Inconsistent Weld Quality: This may be attributed to misalignment or incorrect power settings. Checking the alignment and recalibrating the machine often resolves the issue.
- Overheating: Ensure that the cooling system is operational. Keeping the machine clean and well-ventilated can also prevent overheating.
- Software Glitches: Restarting the system and ensuring the software is up-to-date often rectifies these issues.
Upgrading Technology: When and How?
Technology in laser welding is continuously evolving. Knowing when to upgrade is crucial for maintaining competitiveness. Signs that it might be time for an upgrade include:
- Increased Downtime: Frequent breakdowns or maintenance issues indicate that the machine may be nearing the end of its feasible operational life.
- Poor Efficiency: If the output does not meet market demands, newer models may offer improved speed, accuracy, or features that can help your production.
- Inability to Process New Materials: As manufacturing materials evolve, the need to work with advanced composites or alloys may necessitate newer technology.
Before upgrading, conduct a thorough analysis of your operational needs and potential return on investment. It’s also advisable to seek expert consultation to select the best options available.
Future Trends in Laser Welding Machine Technology
Advancements in Automation for Laser Welding Machine
The integration of automation in laser welding is a significant trend, driven by the need for increased efficiency and reduced labor costs. Automated laser welding systems, including robotics, allow for high-speed production and minimal human intervention.
Automation not only increases productivity but also improves precision, as robotic systems can handle repetitive tasks with greater accuracy than their manual counterparts. This shift towards automation is especially beneficial in high-volume production environments, where consistency and reliability are paramount.
Integration with Industry 4.0
The concept of Industry 4.0 encompasses smart factories where machines are interconnected and capable of communicating with each other. Laser welding machines are increasingly being integrated into these systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and data analysis.
With advanced sensors and IoT capabilities, manufacturers can assess machine performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize processes dynamically. This integration fosters a proactive approach to operations, paving the way for greater efficiency and cost savings.
Environmental Considerations in Laser Welding Machine Use
As sustainability becomes a priority in industrial operations, laser welding machines are gradually seen as eco-friendlier alternatives to traditional welding methods. They typically require less energy and produce fewer emissions, contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
Moreover, the precision of laser welding decreases material wastage, as less material is needed to create a high-quality weld. Manufacturers are encouraged to adopt practices that further enhance sustainability, such as recycling waste materials and optimizing energy consumption during operations.












Leave a Reply