Understanding Electrical Equipment Testing
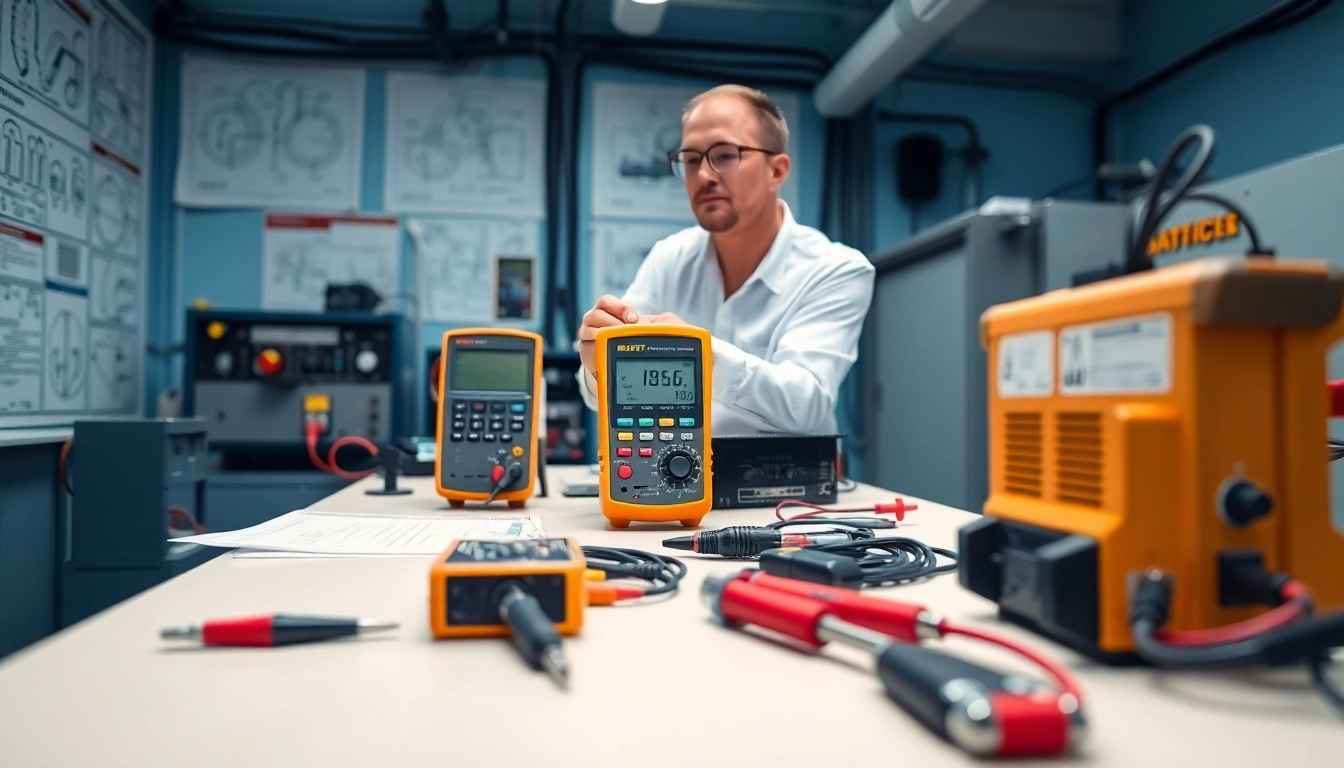
Electrical equipment testing refers to the systematic evaluation of electrical systems, devices, and components to ensure their operation aligns with industry standards and safety regulations. Whether in commercial, industrial, or residential settings, regular testing is crucial for maintaining electrical integrity and preventing potential hazards. It encompasses a variety of processes to assess performance reliability and electrical safety. As you navigate the landscape of electrical systems, leveraging Electrical Equipment Testing can significantly enhance operational safety and efficiency.
What is Electrical Equipment Testing?
Electrical equipment testing is a process that involves several examination techniques to validate the performance and safety of electrical devices. This process not only checks if the equipment operates correctly but also assesses compliance with applicable regulations and standards. The testing can range from simple voltage checks to comprehensive evaluations involving multiple parameters such as insulation resistance, continuity, and functionality. Each piece of equipment, whether it be a transformer, switchgear, or circuit breaker, demands specific tests tailored to its function and use-case scenarios.
Importance of Electrical Equipment Testing
The significance of electrical equipment testing cannot be overstated. Firstly, it ensures safety by preventing electrical shocks, fires, and other hazards. Regular testing and maintenance can identify potential faults before they escalate, ensuring that equipment operates within designed parameters, thus extending its lifespan. Secondly, it helps organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements, minimizing liability risks due to accidents caused by faulty equipment. Furthermore, regular testing enhances reliability and efficiency, resulting in reduced downtime and maintenance costs in the long run.
Common Standards and Regulations
The electrical testing landscape is governed by numerous standards and regulations, critical for ensuring safety and performance. Among the most recognized standards are the National Electrical Code (NEC), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standards, and international standards such as those from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Compliance with these regulations demands a deep understanding of their nuances, which can significantly influence testing methodologies and reporting. By adhering to these standards, organizations can ensure that their electrical systems meet safety and quality benchmarks, fostering a culture of excellence and safety.
Types of Electrical Equipment Testing
Diverse testing methods exist, tailored to meet the specific needs of different electrical devices. Understanding these testing types helps organizations select the appropriate solutions for their unique environments and applications.
Insulation Resistance Testing
Insulation resistance testing is essential in evaluating the effectiveness of insulation in electrical systems. This test measures the resistance offered by insulation material against electric current, indicating potential degradation or failure. A high insulation resistance value usually correlates with good insulation health, while lower values may suggest wear or moisture ingress. It’s crucial for facilities to conduct these tests regularly, especially in environments prone to humidity or chemical exposure, as they can preempt electrical failures and ensure operational safety.
Continuity Testing
Continuity testing is another vital aspect of electrical equipment testing. This method checks if electrical paths are complete and that connections are secure. It is often performed using a multimeter or continuity tester that sends a small current through the circuit. Ensuring continuity is particularly important in installations such as power distribution circuits, where secure connections can prevent electrical hazards and ensure reliable operation. Regular continuity checks also reduce the risk of equipment damage caused by open circuits, resulting in fewer unexpected outages.
Functional Testing and Beyond
Functional testing serves to verify that electrical equipment operates correctly according to its specified functions. This type of testing includes initiating devices, measuring their outputs, and discerning their responsiveness to control inputs. Beyond just basic functionality, this testing often extends to load testing, where equipment performance under maximum operating conditions is assessed. Implementing a rigorous functional testing regimen promotes confidence in the equipment’s reliability and identifies any need for maintenance or upgrades before failures arise.
Best Practices for Effective Testing
To ensure successful electrical equipment testing, adherence to best practices is recommended. These encompass selecting appropriate equipment, observing safety precautions, and thoroughly documenting results for regulatory compliance and future reference.
Choosing the Right Equipment
Choosing the correct testing equipment is fundamental to the effectiveness of the testing process. Different tests require specific tools and methodologies. For instance, an insulation resistance tester is essential for insulation evaluations, while a multimeter is adequate for continuity checks. Organizations should invest in high-quality, calibrated testing tools and consider portable options for on-site evaluations, enhancing both flexibility and efficiency. Educating staff on the operations of these tools can further reinforce the accuracy and reliability of test results.
Safety Precautions During Testing
Safety is non-negotiable in electrical equipment testing. Prior to conducting any test, technicians should ensure all necessary precautions are taken, including wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), de-energizing equipment when possible, and adhering to lockout/tagout (LOTO) protocols. Maintaining a clean and organized workspace also reduces the risk of accidents. By implementing rigorous safety procedures, organizations can mitigate hazards that testing may introduce, safeguarding personnel and assets alike.
Documenting and Reporting Results
Comprehensive documentation of testing results is critical for future maintenance and regulatory compliance. Accurate records facilitate a clear understanding of equipment conditions over time, helping to identify potential patterns or recurring issues. This documentation should include detailed descriptions of tests performed, results achieved, and any recommended actions based on findings. Incorporating digital tools for logging and reporting can enhance accessibility and streamline communication across teams, ultimately improving operational efficiency.
Common Challenges in Electrical Equipment Testing
While electrical equipment testing is essential for ensuring safety and operational efficiency, it is not without its challenges. Understanding these obstacles can help organizations mitigate risks associated with testing processes.
Identifying Faults in Electrical Systems
One of the most significant challenges faced during electrical testing is the accurate identification of faults within complex systems. Faults can be intermittent or elusive, making them hard to isolate. To combat this, employing advanced diagnostic tools such as thermal imaging cameras and power quality analyzers can substantially enhance fault detection and diagnose underlying issues. Additionally, continuous training of staff in interpreting data from diagnostic equipment allows for quicker problem identification and resolution.
Adapting to New Technology Standards
The rapid evolution of technology continually introduces new standards and regulations, posing challenges for organizations to keep their testing protocols up to date. Frequent training sessions and certifications can equip staff with the necessary information on emerging technologies and regulatory changes. Furthermore, subscribing to industry news outlets or becoming members of relevant organizations ensures that companies stay ahead of technology trends, enhancing compliance and operational performance.
Mitigating Downtime During Testing
Downtime during testing can be costly for organizations. Scheduling tests during off-peak hours or implementing phased testing can help minimize disruptions. Additionally, having contingency plans in place to quickly revert to service if any unforeseen issues arise can significantly reduce downtime risks. Effective communication about testing schedules with all stakeholders can also foster collaboration and mitigate potential operational delays.
Future Trends in Electrical Equipment Testing
The realm of electrical equipment testing is continuously evolving, influenced by advancements in technology and changing market needs. Understanding future trends can help organizations adapt and thrive in a competitive landscape.
Integration of Smart Technology
As the demand for smart technology increases, its integration into electrical equipment testing processes becomes inevitable. Smart devices equipped with IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities can provide real-time data on equipment performance, helping to quickly identify issues and enhance preventive maintenance strategies. This trend not only boosts operational efficiency but also allows for more agile responses to electrical failures, ultimately saving time and resources.
Remote Testing Solutions
The rise of remote work and digital connectivity has paved the way for remote testing solutions. Utilizing online platforms and instrumentation with remote access features enables technicians to conduct tests and monitor performance from various locations. This trend promotes greater versatility and can significantly reduce travel costs while maintaining high standards of service delivery, allowing organizations to leverage expertise without geographical constraints.
Regulatory Changes and Their Impact
Regulatory changes are a constant in the electrical industry, and organizations must remain adaptable. Staying informed about new regulations and actively participating in industry groups can equip businesses to anticipate changes rather than react. This proactive approach ensures compliance and safeguards against potential fines or operational disruptions associated with outdated practices. Adapting to these changes may also prompt organizations to invest in more energy-efficient technologies that align with modern compliance requirements, further enhancing their marketability and performance.













Leave a Reply